Banking Issues in Focus provides an in-depth analysis of topical banking issues. These articles range from timely analysis of economic and banking trends at the national and regional level that may affect the risk exposure of FDIC-insured institutions to research on issues affecting the banking system and the development of regulatory policy.
In the past, these articles were featured in FDIC Quarterly Volumes.
Recent Articles
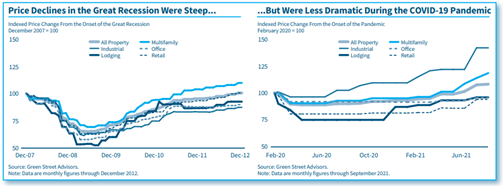
Commercial Real Estate: Resilience, Recovery, and Risks Ahead
By Jeffrey Ayres, Robert DiChiara, Alexander Gilchrist, James Presley-Nelson and Stephen Simpson (2021)
Commercial real estate (CRE) lending is important to the banking industry, which holds $2.7 trillion in CRE loans. In the pandemic, CRE conditions in several property types came under stress. The pandemic challenged the brick-and-mortar retail, hotel, and office sectors, while multifamily largely held up and the industrial sector benefitted from increased demand. Market conditions improved with economic recovery in 2021, but some of the changes the CRE industry experienced in the pandemic may be long-lasting. The issues facing CRE will be important considerations for a large share of the banking industry. Initially the pandemic threatened to significantly challenge banks’ CRE loan quality, but loan delinquency rates remained low through third quarter 2021 against the backdrop of economic rebound, stimulus support, and loan forbearance. This article analyzes conditions across major CRE property types and discusses FDIC-insured institutions’ exposure to CRE loans, credit quality, and potential challenges ahead.
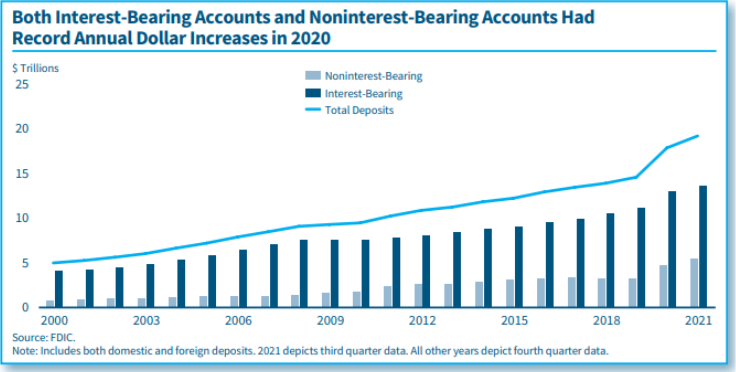
Implications of Record Deposit Inflows for Banks During the Pandemic
By Caitlyn Kasper and Benjamin Tikvina (2021)
In 2020, the pandemic disrupted the global economy, creating stress and uncertainties for consumers and businesses. The U.S. government responded with assistance programs that, combined with increased personal savings, contributed to a record inflow of deposits to banks. The deposit inflows created historically high bank liquidity and many banks shifted their balance sheet composition to shorter-term, lower-yielding and non-yielding assets. The shift in asset composition and a prolonged period of low interest rates caused the net interest margin to decline to its lowest level on record. The loans-to-deposits ratio reached record lows in 2020 and 2021, while the cash-to-deposits ratio rose to 1.6 times the pre-pandemic level and almost three times the previous trough in 2006. Benefits of higher liquidity include reduced dependence on less stable sources of funding and an ability to respond to unforeseen deposit account withdrawals. However, higher liquidity can also challenge bank earnings, depending on loan demand and the shape of the yield curve.
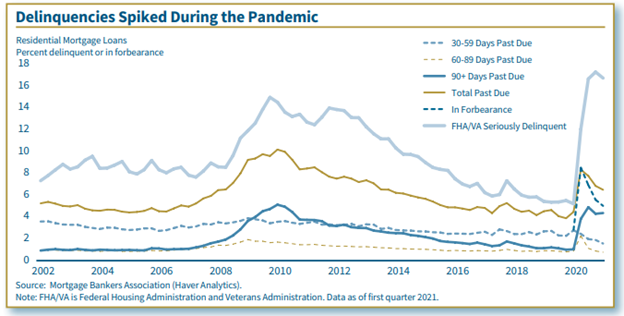
Residential Lending During the Pandemic
By Cynthia Angell (2021)
The housing market rebounded from the COVID-19 pandemic-induced recession faster than other sectors of the economy, helped by historically low interest rates and fiscal support. Still, weaker economic fundamentals led to tightening of mortgage credit and underwriting standards as lenders sought to reduce credit risk from new mortgages. Mortgage credit performance improved after deteriorating at the start of the pandemic, but high rates of delinquent loans reflect lingering financial distress for many borrowers. The coming expiration of federal programs that have aided homeowners raises concern about the possible increased risk of mortgage credit quality deterioration and reduced credit availability. Nevertheless, banks have been resilient and, despite the uncertain outlook, continue to extend residential loans.
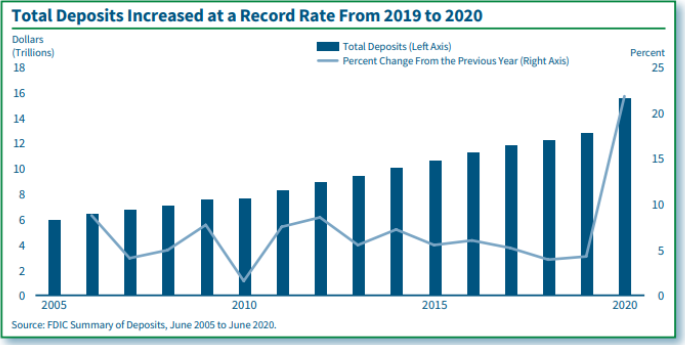
2020 Summary of Deposits Highlights
By Joseph Harris III, Caitlyn Kasper, Camille Keith and Derek Thieme (2021)
The 2020 Summary of Deposits Survey showed deposit growth of 21.7 percent between June 2019 and June 2020, the largest one-year increase in nearly 80 years. The large year-overyear increase in deposits occurred primarily in the first two quarters of 2020, and was likely driven by reactions of individuals, businesses, and U.S. fiscal and monetary authorities to the COVID-19 pandemic. Deposits increased the most for noncommunity banks, midsize banks, banks with a mortgage lending specialization, and offices in metropolitan counties. The number of bank offices declined for the 11th consecutive year but at a lower rate than in the previous three years. The relatively low rate of decline in the number of offices was influenced by a low rate of closures among offices acquired through mergers. Further, the number of noncommunity bank offices and offices in metropolitan counties declined at low rates from June 2019 to June 2020 compared to previous years.
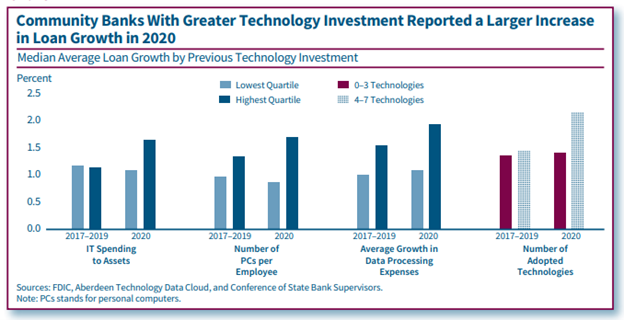
The Importance of Technology Investments for Community Bank Lending and Deposit Taking During the Pandemic
By Daniel Hoople (2021)
Community banks that invested more in technology generally reported faster loan and deposit growth in 2020 than did banks with less technology investment. Moreover, the differences in loan and deposit growth associated with technology investment were greater in 2020 than the differences reported prior to the pandemic. Faster loan growth for community banks with greater technology investment largely stemmed from participation in the Paycheck Protection Program (PPP). These community banks, on average, originated a greater share of PPP loans regardless of the loan size, origination date, or borrower distance from the nearest bank branch. Meanwhile, the larger increases in deposit growth of community banks that invested more in technology were due to increases in deposit balances of existing customers rather than from new depositors.